 Dr. Philip Siegmann
Dr. Philip Siegmann| Contact |
Research |
Publications |
Teaching |
Software |
Links |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Dr. Philip Siegmann Dr. Philip Siegmann |
|||||
Research
(a)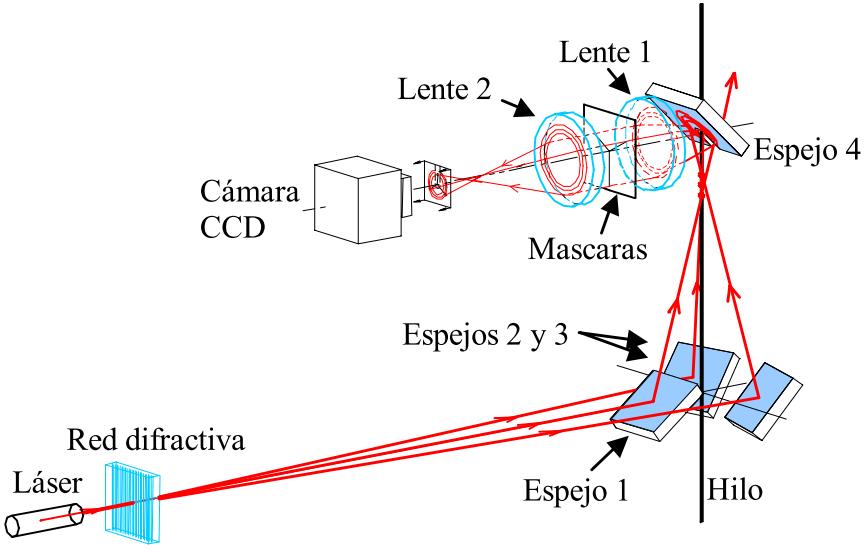 |
(b)
 |
(c)
 |
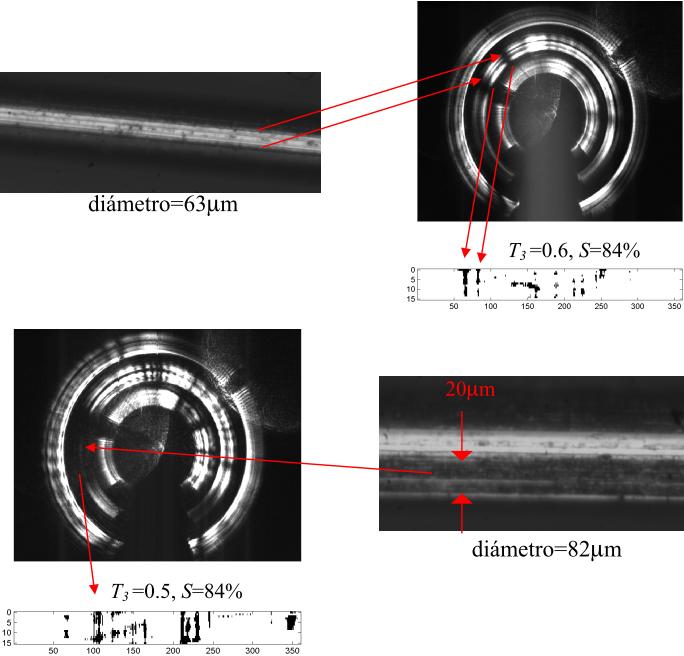
| Fig.
1. a) Optical device for 360º wire surface inspection (patent reference [1]). b) The surface
defects are detected as fluctuations in the intensity profiles of the
conical reflected beam. c) Example of in-line implementation and image processing. |
||
(a)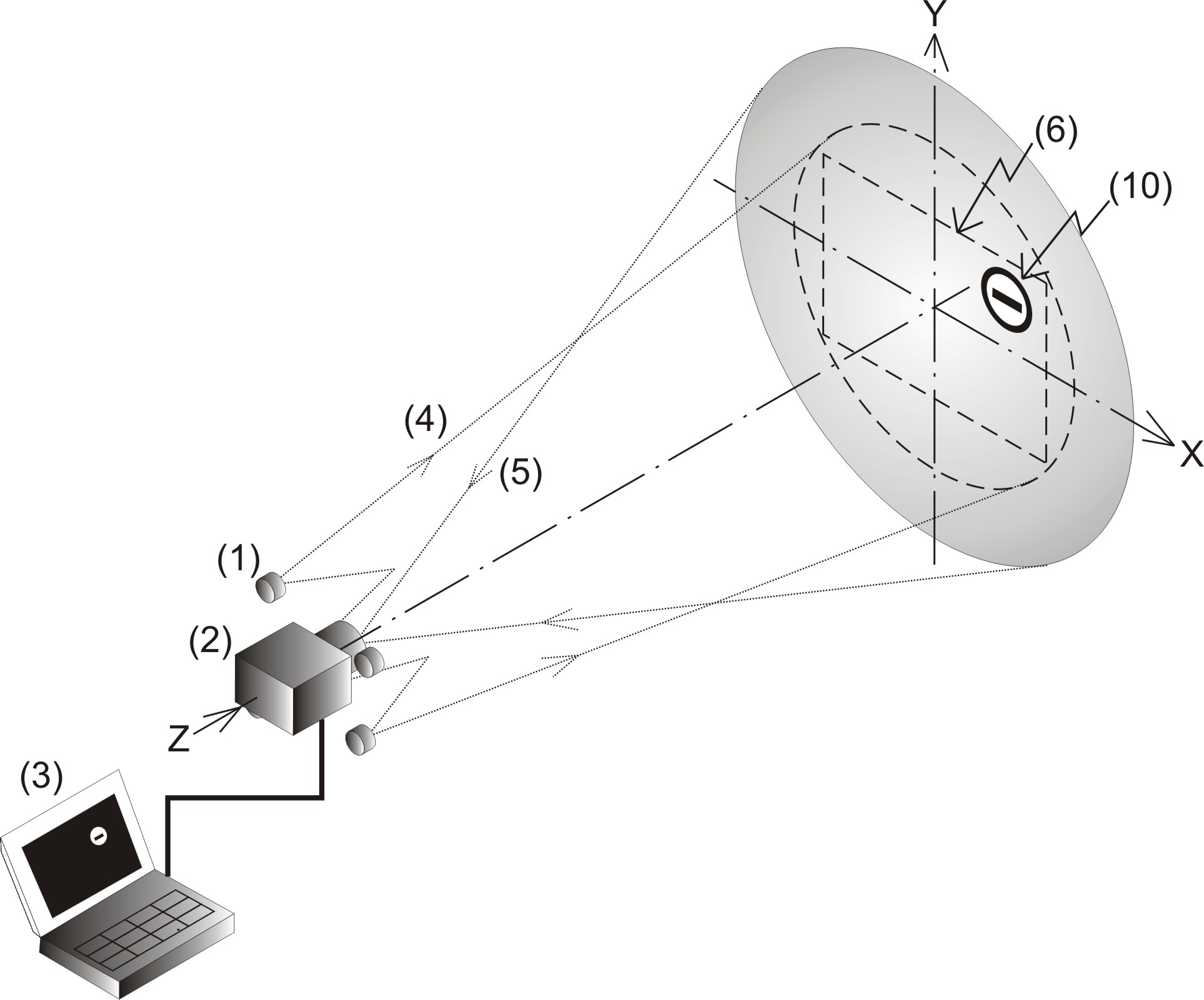 |
(b) |
(c)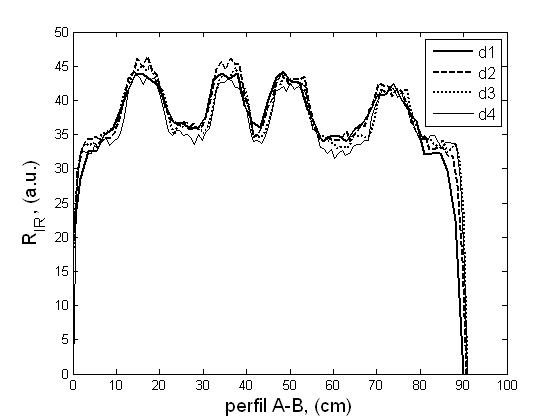 |
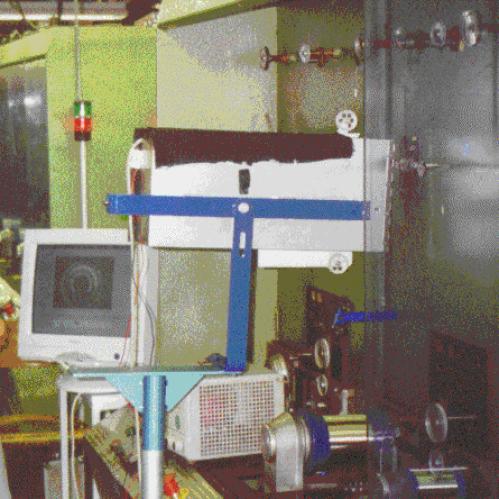
| Fig.
2. a) Scheme of the optical device for retroreflectivity measurements.
b) Example of measured retroreflectivity of a traffic sign, and c) profile A-H at different
distances to the device (d1=20>d2>d3>d4=10m). |
||
(a)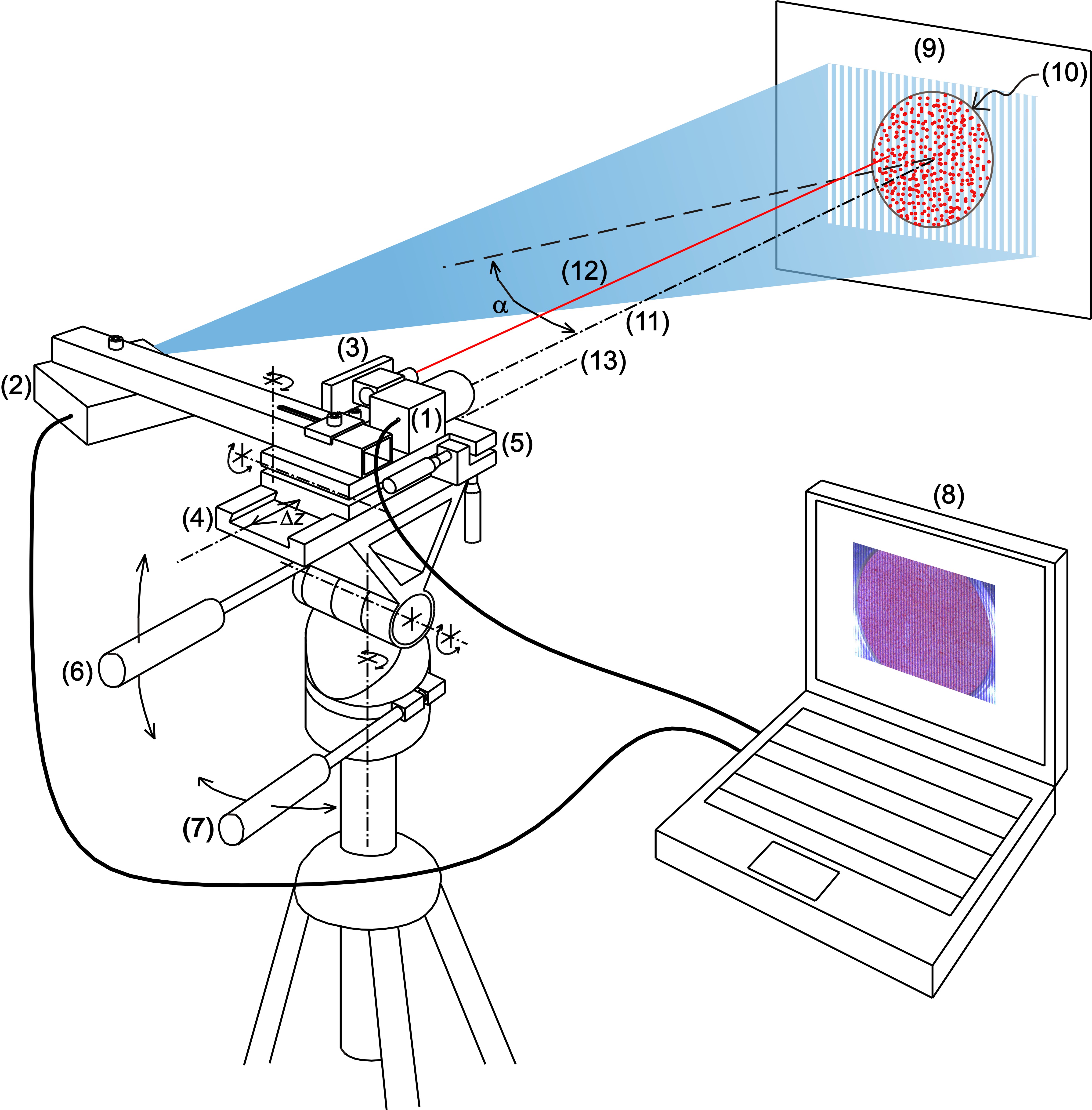 |
(b)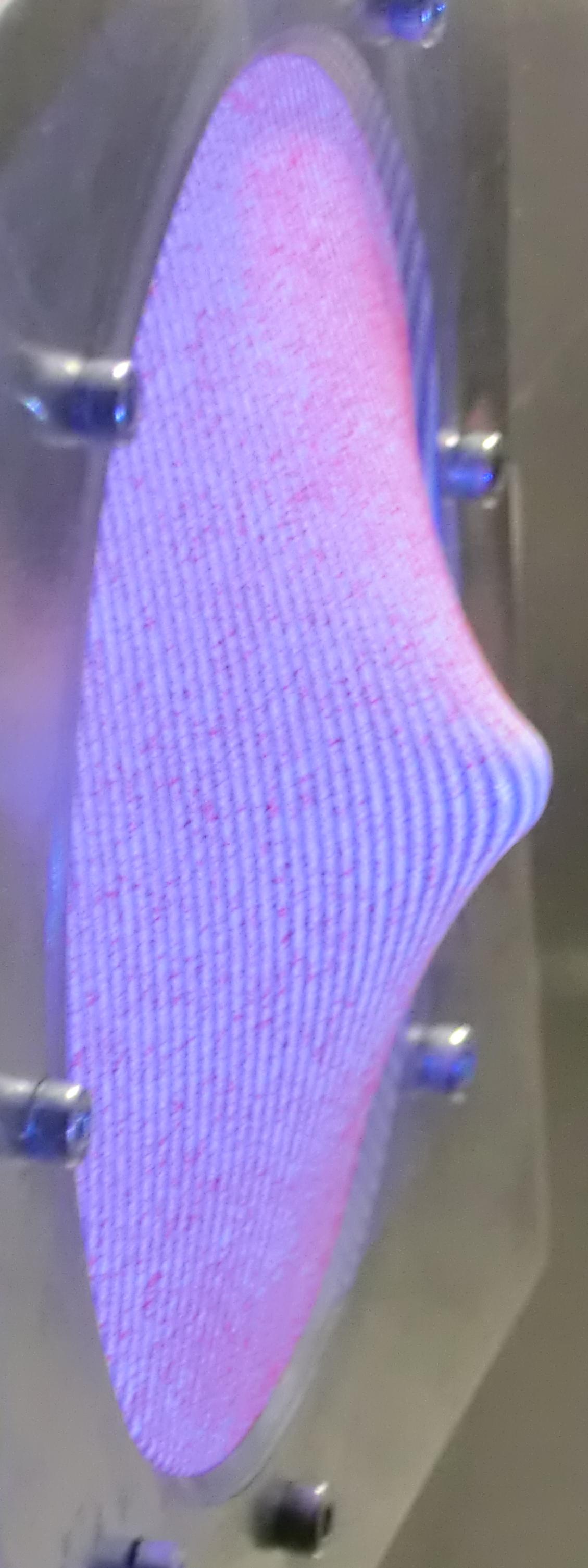
|
(c)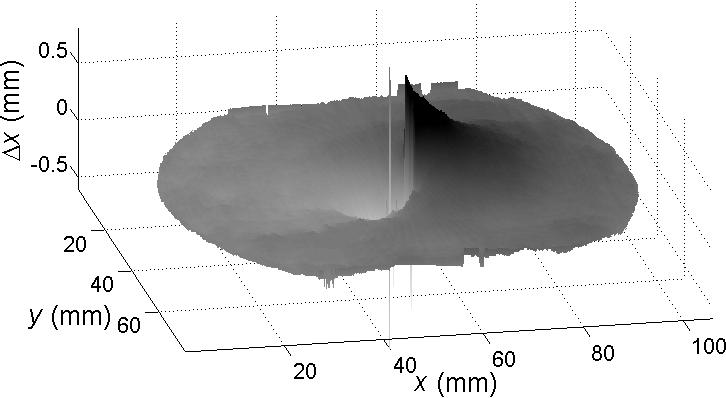 (d) 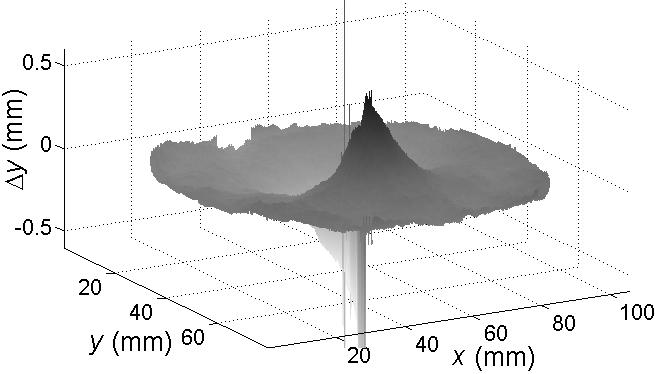 |
(e)
|
|
| Fig.
3. a) Scheme of the device for simultaneous measurements of
in- and out-of-plane displacements. b) Example of a
deformed elastic membrane and c) to e) the obtained displacements in each spatial
direction. |
||||
|
(a)
 |
(b)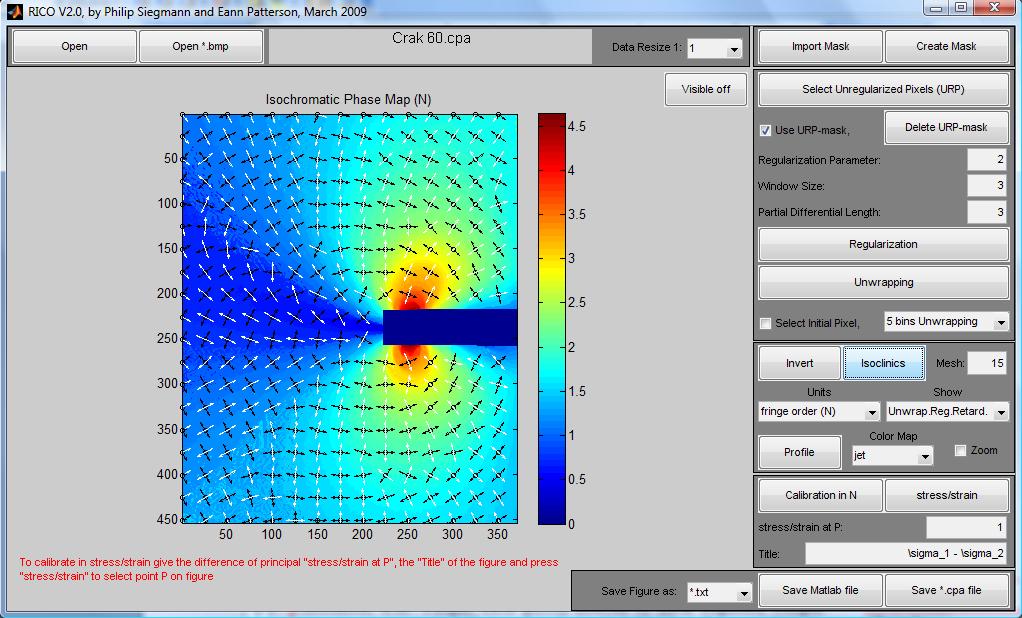 |
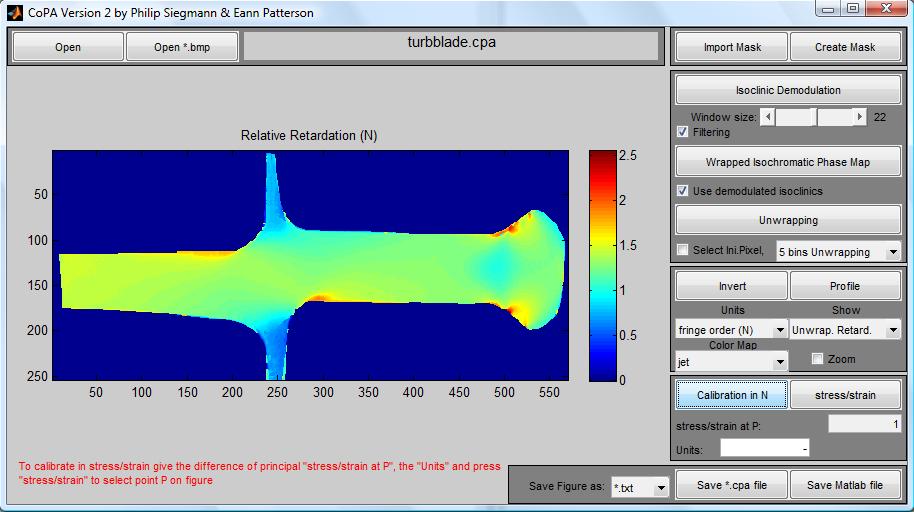
| Fig.
4. Grafic User Interface s of a) COPA and b) RICO (writen in MATLAB)
showing examples of processed data: a) section of a turbine blade
and b) acrack propagation (CT test). |
|
(a)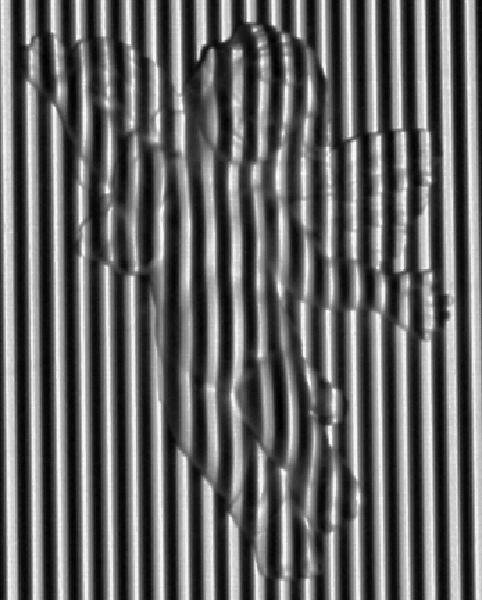 |
(b)
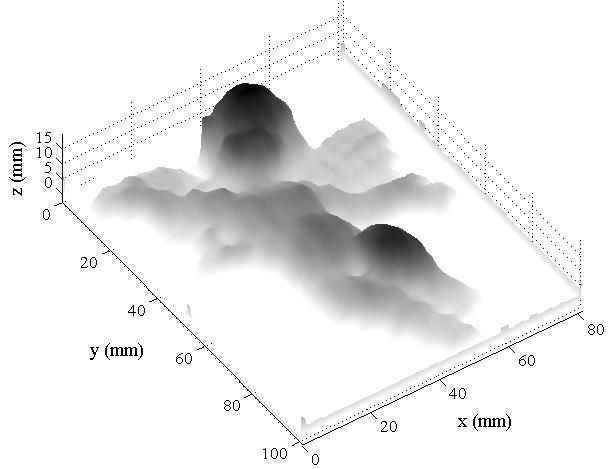 |
| Fig. 5. a) Image of an angel with projected fringes. b) 3D reonstruction of the angel using 5 phase shifted Fringe Projection technique. | |
|
(a)
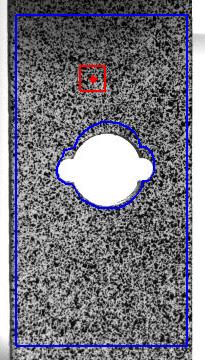 |
(b)
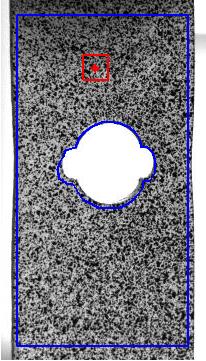 |
(c)
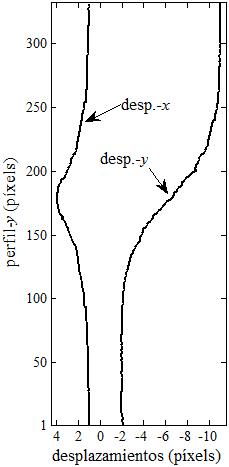 |
(d)
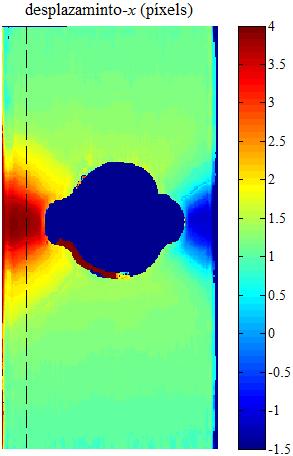 |
(e)
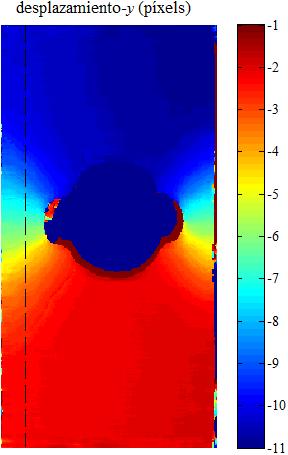 |
| Fig.
6. Example of 2D-DIC. a) Unloded sample. b) Verticaly streched sample.
c) Profiles along the vertical lines shown on the x-displacement map
(d) and y-displacement map (e). |
||||
Signal Processing
(a)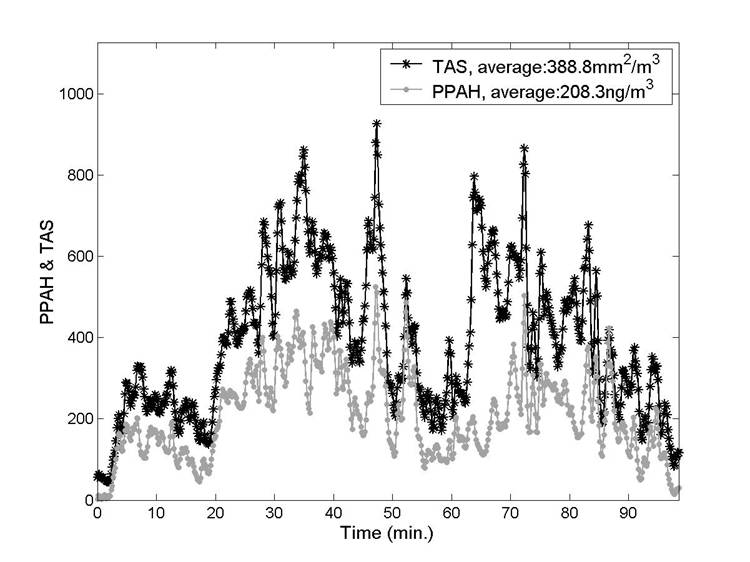 |
(b)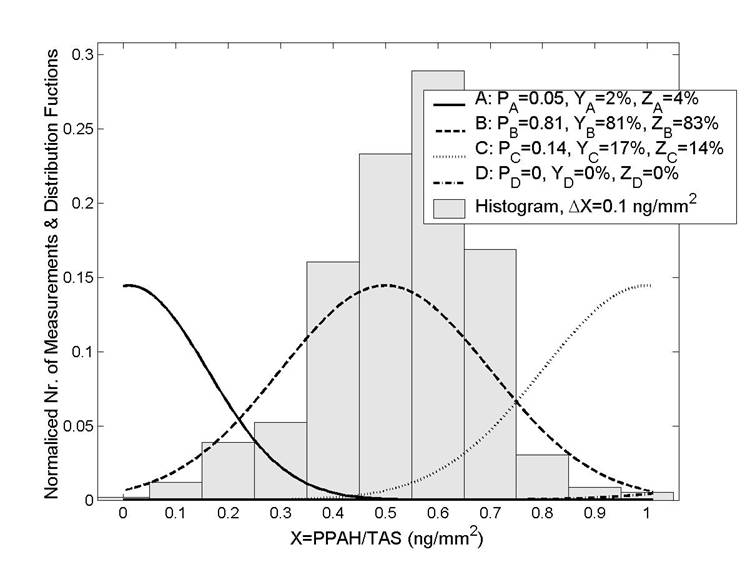 |
| Fig. 7. a) Example of a field measurement (TAS: Total Active Surface and
PPAH: Particle-bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydicarbons) along the roads
of Madrid year 2006. b) By applying the PSA method to the measurements
in (a), we obtain thant 81% of the measured data can be associated to
source type B (fresh exhaust aerosol emmited from diesel vehicles). |
|
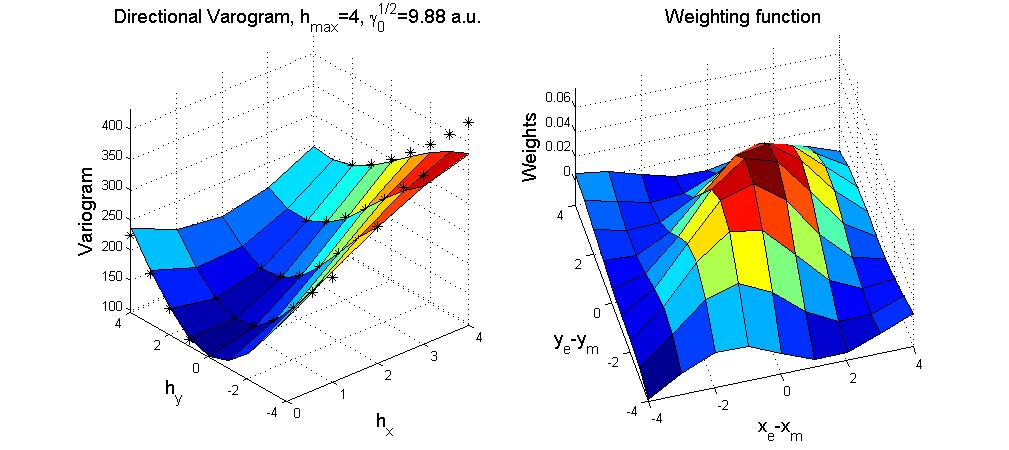 |
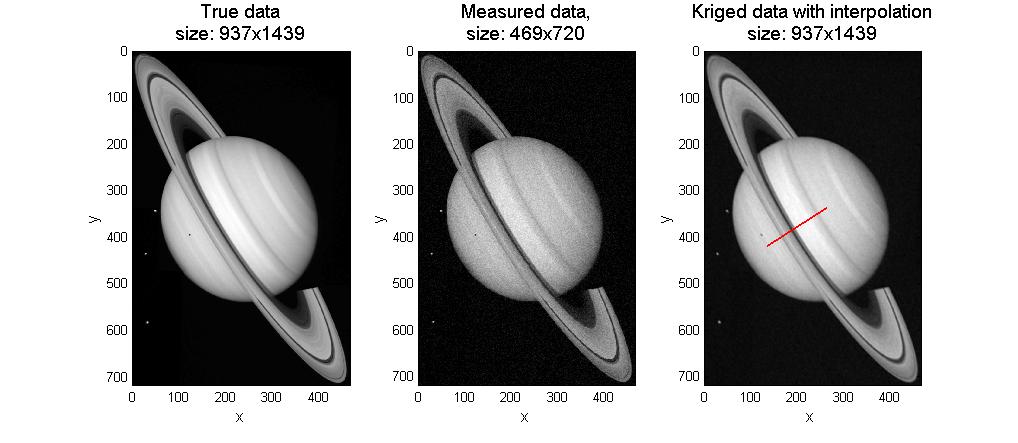  |
| Fig. 8. To estimate the true data from the measured data, we compute first the weigthing factors which are obtained from the directional variogram. The weighting factors are used to estimate the noise free values
at any position. The measured data is sampled, noisy and also
convoluted with the finite detector size (e.g. pixel size). After
estimating a higher resoluted and noise free data a deconvolution is
necesary if the true data is to be recovered. |